Virtualization
Updated: Tue, 24 Mar 2015 by Rad
Virtualization - inn computing, virtualization means to create a virtual version of a device or resource, such as a server, storage device, network or even an operating system where the framework divides the resource into one or more execution environments
Devices, applications and human users are able to interact with the virtual resource as if it were a real single logical resource.
Virtualization began in 1960s mainframe computers as a method of logically dividing the system resources provided by mainframes between different applications. Since then, the meaning of the term has broadened
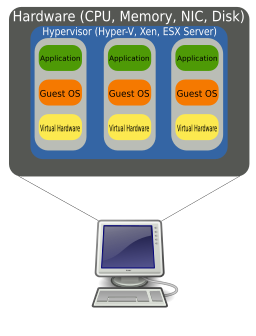
Hardware virtualization
Hardware virtualization or platform virtualization refers to the creation of a virtual machine that acts like a real computer with an operating system. Software executed on these virtual machines is separated from the underlying hardware resources.
Different types of hardware virtualization include:
- Full virtualization
- Partial virtualization
- Paravirtualization
Source: By John Aplessed (Own work), Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Reducing the costs
Virtualization is the single most effective way to reduce IT expenses while boosting efficiency and agility.
Virtualization lets you:
- Run multiple operating systems and applications on a single server.
- Consolidate hardware to get vastly higher productivity from fewer servers.
- Save 50 percent or more on overall IT costs.
- Speed up and simplify IT management, maintenance, and the deployment of new applications.
Top virtualization industry players (2014, 2015)
- VMware
- Citrix
- HP
- Cisco
- Microsoft
- Red Hat
- Amazon
Virtualization challenges
Virtualization now accounts for one-half of all server workloads and it should reach more than 85 percent by 2016, according to Gartner.
The benefits are many:
- Virtualization can reduce server incidents by 27 percent,
- System downtime by 26 percent and
- App-to-market time by 22 percent
There is no doubt about the numerous advantages virtualization brings. However, that's not all a business should pay attention to when looking to adopt virtualization:
Virtualization challenges:
- Security
- Backup and recovery
- VM Sprawl
- Capacity Planning
- VM Stall
- Licensing restrictions
Desktop virtualization
Desktop virtualization is software technology that separates the desktop environment and associated application software from the physical client device that is used to access it.
Desktop virtualization implementations are classified based on whether the virtual desktop runs remotely or locally. It is important to note that not all forms of desktop virtualization involve the use of virtual machines (VMs).
Desktop virtualization provides many benefits, not the least of which is reducing maintenance costs:
- Ease and Comfort - can work from anywhere
- Secure, mobile access to applications
- Flexibility
- Ease of maintenance
- Desktop security
- Reduced costs
< back to glossary
Virtualization from around web
- Virtualization
- 7 Virtualization Challenges
- Eight Top Challenges of Virtualization Management
- Virtualization
< back to glossary